Assignment from Mr. Tri Djoko Wahjono, Ir., M.Sc.
Name : Tommy Hendrawan
NIM / Class : 1701309513 / 01PCT
Assignment : Discovering Computer 2011 - Chapter 8 Operating Systems & Utility Programs
1. What Is System Software, and What Are the Two Types of
System Software?
System software consists of the programs that control or
maintain the operations of a computer and its devices. Two types of system
software are operating systems and utility programs. An operating system (OS)
is a set of programs containing instructions that work together to coordinate all
the activities among computer hardware resources. A utility program, also called
a utility, performs maintenance-type tasks, usually related to managing a
computer, its devices, or its programs.
2. What Are the Functions of an Operating System?
The operating system starts and shuts down a computer, provides
a user interface, manages programs, manages memory, coordinates tasks, configures
devices, establishes an Internet connection, monitors performance, provides utilities,
updates automatically, controls a network, and administers security. The user
interface controls how data and instructions are entered and how information is
displayed on the screen. Two types of user interfaces are a graphical user
interface (GUI) and a command-line interface. Managing programs refers to how
many users, and how many programs, an operating system can support at one time.
An operating system can be single user/single tasking, single user/multitasking,
multiuser, or multiprocessing. Memory management optimizes the use of random
access memory (RAM). If memory is insufficient, the operating system may use
virtual memory, which allocates a portion of a storage medium to function as
additional RAM. Coordinating tasks determines the order in which tasks are
processed. Tasks include receiving data from an input device, processing
instructions, sending information to an output device, and transferring items
between storage and memory. Configuring devices involves loading each device’s
driver when a user boots the computer. A driver, short for device driver, is a
small program that tells the operating system how to communicate with a specific
device. Establishing an Internet connection sets up a connection between a
computer and an Internet access provider. A performance monitor is an operating
system program that assesses and reports information about computer resources
and devices. Operating systems often provide the capability of managing and searching
for fi les, viewing images, securing a computer from unauthorized access, uninstalling
programs, and other tasks. Most operating systems also include an automatic update
feature that provides updates to the program. A server operating system is an
operating system that organizes and coordinates how multiple user’s access and
share network resources. Network administrators typically have an administrator
account that enables them to access fi les, install programs, and specify
network settings, including creating user accounts and establishing permissions.
3. What Is the Startup Process on a Personal Computer?
Booting is the process of starting or restarting a computer.
When a user turns on a computer, the power supply sends a signal to the system
unit. The processor chip finds the ROM chip(s) that contains the BIOS (basic
input/output system), which is firmware with the computer’s startup instructions.
The BIOS performs the power-on self-test (POST) to check system components and
compares the results with data in a CMOS chip. If the POST completes successfully,
the BIOS searches for the system files and the kernel of the operating system, which
manages memory and devices, and loads them into memory from storage. Finally,
the operating system loads configuration information, requests any necessary
user information, and displays the desktop on the screen. The operating system
executes programs in the Startup folder, which contains a list of programs that
open automatically when you boot the computer.
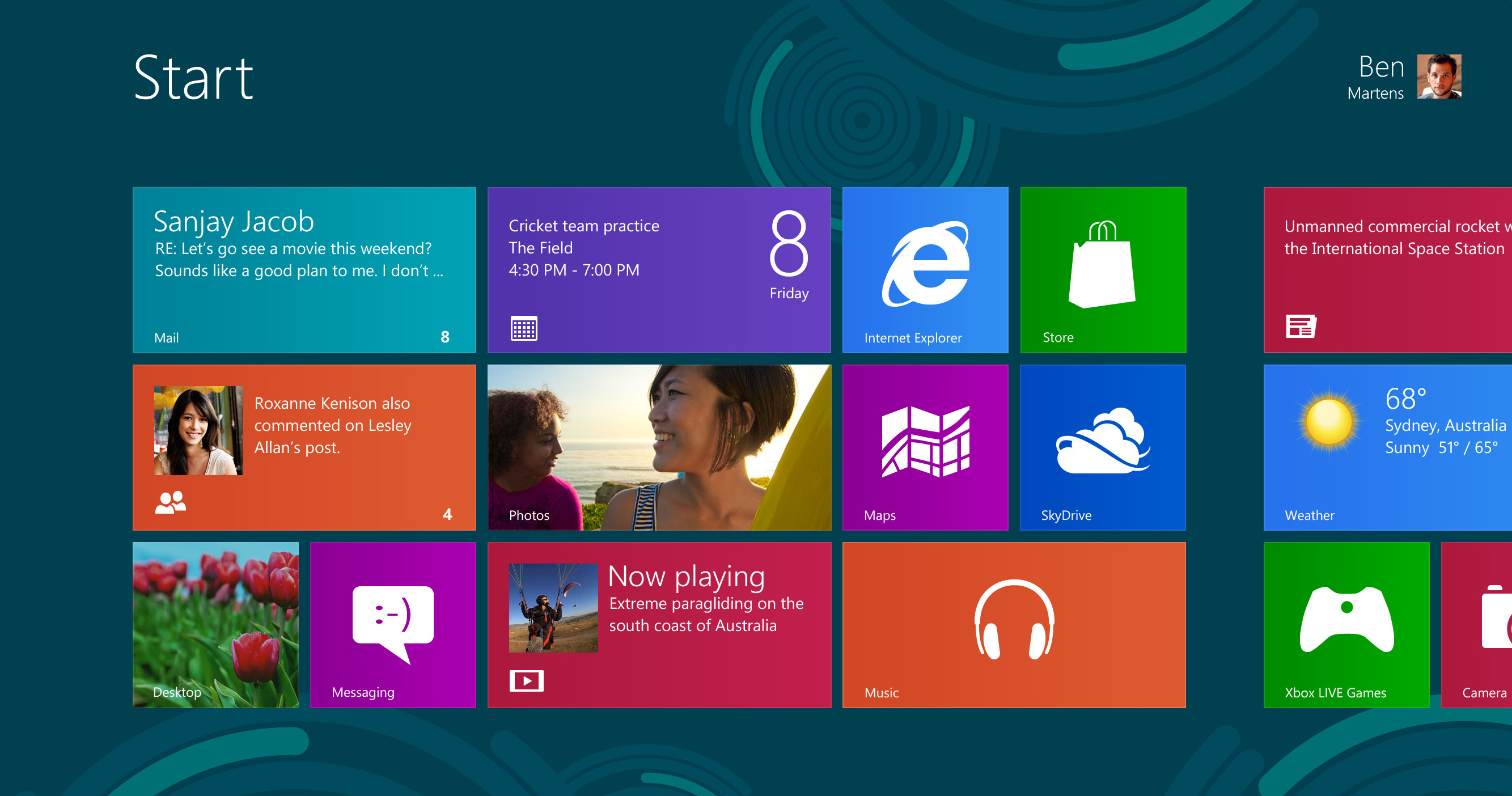
4. What Are Features of Windows 7, Mac OS X, UNIX, and Linux
Operating Systems?
A stand-alone operating system is a complete operating
system that works on a desktop computer, notebook computer, or mobile computing
device. Windows 7 is Microsoft’s fastest, most efficient operating system to
date, offering quicker program start up, built-in diagnostics, automatic recovery,
improved security, enhanced searching and organizing capabilities, and an
easy-to-use interface. Most users choose from Windows 7 Starter, Windows 7 Home
Premium, Windows 7 Ultimate, or Windows 7 Professional editions. Mac OS X is a
multitasking operating system available only for Apple computers. UNIX is a
multitasking operating system developed at Bell Laboratories. Linux is a
popular, multitasking UNIX-type operating system that is open source software, which
means its code is available to the public for use, modification, and
redistribution.
5. What Are Various Server Operating Systems?
 |
| http://www.omgchrome.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/windows8.jpg |
Server operating systems include Windows Server 2008, UNIX,
Linux, Solaris, and NetWare. Windows Server 2008 is an upgrade to Windows
Server 2003 and includes features of previous Windows Server versions. UNIX,
like Linux, is a multipurpose operating system because it is both a stand-alone
and server operating system. Solaris, a version of UNIX developed by Sun Microsystems,
is a server operating system designed specifically for e-commerce applications.
Novell’s NetWare is a server operating system designed for client/server
networks.
6. What Are the Features of Several Embedded Operating Systems?
Mobile devices and many consumer electronics have an
embedded operating system that resides on a ROM chip. Popular embedded operating
systems include Windows Embedded CE, Windows Mobile, Palm OS, iPhone OS,
BlackBerry, Google Android, embedded Linux, and Symbian OS. Windows Embedded CE
is a scaled-down Windows operating system designed for use on communications, entertainment,
and computing devices with limited functionality. Windows Mobile, an operating
system based on Windows Embedded CE, provides a user interface designed for specific
types of smart phones and PDAs. Palm OS is an operating system used on smart
phones and PDAs. iPhone OS, developed by Apple, is an operating system for the iPhone
and iPod touch. The BlackBerry operating system runs on handheld devices
supplied by RIM. Google Android is an operating system developed by Google for mobile
devices. Embedded Linux is a scaled-down Linux operating system for smart
phones, PDAs, portable media players, and other devices requiring an embedded operating
system. Symbian OS is an open source multitasking operating system designed for
smart phones.
7. What Is the Purpose of Several Utility Programs?
Most operating systems include several built-in utility programs.
A file manager performs functions related to fi le management. A search utility
attempts to locate a fi le on your computer based on criteria you specify. An image
viewer displays, copies, and prints the contents of a graphics fi le, such as
photos. An uninstaller removes a program and any associated entries in the system
fi les. A disk cleanup utility searches for and removes unnecessary fi les. A
disk defragmenter reorganizes the fi les and unused space on a computer’s hard
disk. A backup utility is used to copy, or back up, selected fi les or an entire
hard disk to another storage medium. A restore utility reverses the backup process
and returns backed up fi les to their original form. A screen saver displays a
moving image or blank screen if no keyboard or mouse activity occurs for a specified
time. A personal firewall detects and protects a personal computer from
unauthorized intrusions. An antivirus program protects computers against a
virus, or potentially damaging computer program, by identifying and removing
any computer viruses. A spyware remover detects and deletes spyware and other
similar programs. An adware remover detects and deletes adware. Internet filter
programs can include Web filtering software, an anti-spam program, a phishing
filter, and a pop-up blocker. A file compression utility shrinks the size of a
fi le so that it takes up less storage space. A media player allows you to view
images and animation, listen to audio, and watch video fi les on a computer. Disc
burning software writes text, graphics, audio, and video fi les on a recordable
or rewritable CD, DVD, or Blu-ray Disc. A personal computer maintenance utility
identifies and fixes operating system problems and improves a computer’s
performance.









0 komentar:
Posting Komentar